The Silent Threat: Visceral Fat and Health
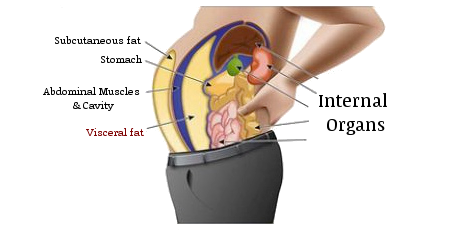
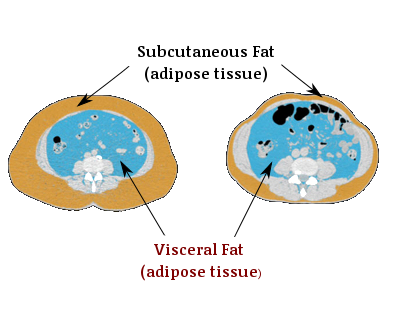
Excess abdominal fat, contributing to the infamous “belly bulge,” can indeed be a primary factor leading to obesity. However, an important distinction must be made here. One can be overweight or obese with a high Body Mass Index (BMI), which are signs of excess fat, but it’s the visceral fat that could be the silent, more dangerous enemy.
Interestingly, even individuals who are not excessively overweight or do not have a high BMI could still harbor substantial amounts of visceral fat. They might have enough visceral fat around their organs to increase their risk of developing serious health conditions like diabetes and heart disease, making them ‘skinny fat’. This phenomenon underscores the insidious nature of visceral fat—it can creep up on us without any evident signs.
In our quest for quick fixes in the modern age, many resort to procedures like liposuction surgery to remove excess fat. However, it is crucial to note that visceral fat cannot be removed through liposuction. Studies have shown that liposuction surgery neither reduces the risk of high blood pressure and cholesterol nor does it improve insulin sensitivity. The only viable and sustainable approach to reducing visceral fat involves lifestyle modifications, including changes in diet and physical activity.
The Dietary Approach: Fighting Visceral Fat with Nutrition
When addressing the issue of visceral fat, it is imperative to discuss the role of diet. The foods we consume have a profound impact on our health and body composition, including the accumulation of visceral fat.
Making mindful dietary choices can be a potent weapon in the fight against visceral fat. The first step in this journey is understanding portion control. It’s not just about what you eat, but also how much you eat. Eating smaller meals throughout the day, rather than three large meals, can help manage hunger and avoid overeating.
Nutrient-rich foods, particularly those high in complex carbohydrates, should form the backbone of your diet. These include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and pulses. Complex carbohydrates are digested slowly, providing a steady source of energy, keeping you full for longer, and helping to control blood sugar levels.
On the other hand, simple carbohydrates found in refined grains, bread, and sugars should be minimized. These foods are digested quickly, leading to rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, promoting hunger and overeating, and contributing to the accumulation of visceral fat.
While it might seem counterintuitive to consume fats when aiming to reduce visceral fat, it is essential to note that not all fats are created equal. Some fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, can actually support health and aid in weight management. However, saturated and trans fats, commonly found in processed foods, should be avoided as they can contribute to the buildup of visceral fat and other health issues.
Exercise: A Powerful Ally against Visceral Fat
A well-rounded approach to combating visceral fat should also include regular physical activity. Exercise plays a significant role in burning calories, reducing body fat, and improving overall health. However, not all exercises are equally effective in addressing visceral fat.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), a type of workout that involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or lower-intensity exercise, has been shown to improve glucose metabolism in muscles and enhance insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Importantly, HIIT has been identified as one of the most effective exercises for reducing visceral fat.
While prolonged sessions of running, jogging, step climbers, and elliptical machines can certainly contribute to overall fitness, they may not offer a quantitative advantage over HIIT in terms of visceral fat reduction. This finding doesn’t undermine the value of these exercises, but it does emphasize the efficiency of HIIT in combating visceral fat. Hence, for those with time constraints, HIIT can be an excellent option.
Conclusion
The journey to reducing visceral fat is a long one, but every step you take is a step toward improved health and well-being. Understanding the nature of visceral fat and the ways to manage it can empower you to take control of your health. The strategies discussed in this article—making mindful dietary choices, incorporating regular physical activity, and focusing on overall lifestyle changes—are not only effective in reducing visceral fat but also in promoting overall health. Remember, the journey may be challenging, but the rewards of a healthier and happier life are well worth the effort.
It’s time we unmask this stealthy enemy within us. By acknowledging visceral fat as a potential health risk, we can begin to take the necessary steps to manage it effectively. Let’s commit to a healthier lifestyle today for a better, diabetes-free life tomorrow.