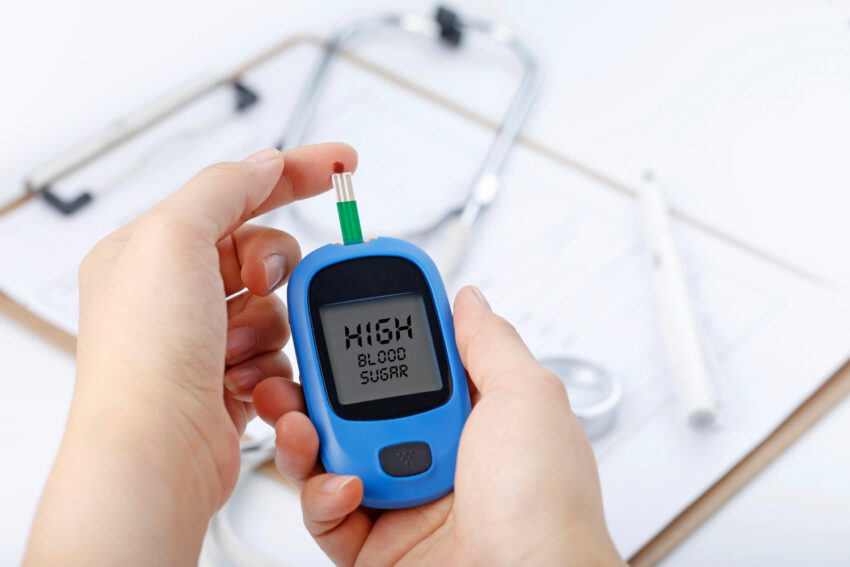
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people around the world. It is caused by a problem with the way the body uses glucose, a type of sugar that is used for energy. Over time, high levels of glucose in the blood can damage the organs and lead to serious complications, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. Managing diabetes carefully is essential to avoid these complications.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of diabetes, how to manage blood sugar levels, and how to prevent and treat common complications.
Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically goes away after delivery.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels is an important part of diabetes management. People with diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and take steps to keep them within a healthy range. This can be done through a combination of diet, exercise, medication, and insulin therapy.
Diet: Eating a healthy diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels. This means consuming plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated and trans fats can also help manage blood sugar levels.

Exercise: Regular exercise is also important for managing blood sugar levels. Exercise helps the body use insulin more effectively and can improve blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Medication: Some people with diabetes may need medication to manage their blood sugar levels. This can include oral medications, such as metformin, or injectable medications, such as insulin.
Insulin Therapy: People with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes may need insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels. Insulin can be injected with a syringe or pen or delivered via an insulin pump.
Preventing and Treating Complications
People with diabetes are at risk of developing a range of complications, including neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. Preventing and treating these complications is an important part of diabetes management.
Neuropathy: Neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur in people with diabetes. Symptoms may include tingling, numbness, and pain in the feet and hands. To prevent neuropathy, it is important to manage blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid smoking. Treatment may include medication to relieve pain or improve nerve function.
Retinopathy: Retinopathy is a type of eye disease that can occur in people with diabetes. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina. To prevent retinopathy, it is important to manage blood sugar levels and get regular eye exams. Treatment may include laser therapy or surgery.
Cardiovascular Disease: People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes. To prevent cardiovascular disease, it is important to manage blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and engage in regular exercise. Treatment may include medication to lower blood pressure or cholesterol.
In conclusion, managing diabetes carefully is essential to prevent complications and improve overall health. This involves monitoring blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine, taking medication as needed, and preventing and treating common complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. If you have diabetes, it is important